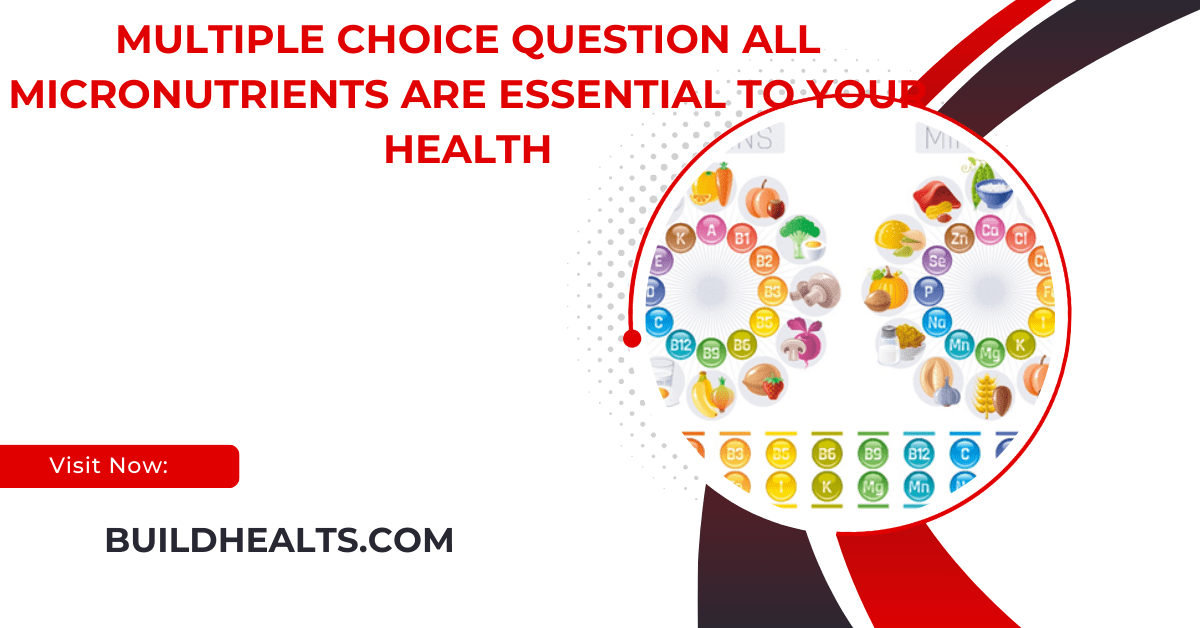
Micronutrients, though needed in small amounts, are essential for immunity, growth, and overall health. This article covers their importance, types, and tips for ensuring proper intake.
Micronutrients play a critical role in maintaining your overall health. Even though they are required in much smaller amounts than macronutrients, they are essential for numerous body functions. From supporting immunity to aiding growth and development, all micronutrients are crucial for maintaining optimal health.
This article will explore the importance of micronutrients, the different types, their specific roles in the body, and how you can ensure you’re getting enough.
Understanding Micronutrients:

Micronutrients are nutrients that are required by the body in small quantities. Despite their small required intake, micronutrients are crucial for various bodily functions. Unlike macronutrients such as carbohydrates, fats, and proteins, which provide energy, micronutrients help regulate body processes, support immune function, and promote overall well-being.
The human body cannot produce most micronutrients, which means they must be obtained through the diet. Micronutrient deficiencies can lead to a range of health problems, including weakened immunity, impaired cognitive function, and poor bone health.
Types of Micronutrients:
Micronutrients can be broadly categorized into two main types: vitamins and minerals. Each category has different functions and is necessary for different aspects of your health.
Vitamins:
Vitamins are organic compounds that the body needs for various biochemical functions. They help in energy production, support the immune system, and aid in the development and maintenance of cells and tissues. There are 13 essential vitamins, which are further divided into two types:
- Water-Soluble Vitamins: These include the B-complex vitamins (B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B7, B9, B12) and vitamin C. Since these vitamins dissolve in water, they are not stored in the body and need to be replenished regularly through diet. Any excess is excreted in urine.
- Vitamin B Complex: These vitamins are essential for converting food into energy, producing red blood cells, and maintaining proper brain function.
- Vitamin C: An important antioxidant that supports immune function and helps the body absorb iron.
Fat-Soluble Vitamins:
These include vitamins A, D, E, and K. Fat-soluble vitamins are stored in the body’s fatty tissues and liver. Since they can accumulate in the body, it’s important to avoid excessive intake.
- Vitamin A: Essential for vision, skin health, and immune function.
- Vitamin D: Critical for calcium absorption and bone health.
- Vitamin E: Acts as an antioxidant, protecting cells from damage.
- Vitamin K: Important for blood clotting and bone metabolism.
Minerals:
Minerals are inorganic elements that are absorbed from soil and water through the plants and animals we consume. Like vitamins, minerals play essential roles in maintaining bodily functions such as building bones, making hormones, and regulating your heartbeat.
Minerals are categorized into two types:
- Major Minerals: These include calcium, magnesium, potassium, sodium, and phosphorus, which are needed in larger amounts.
- Calcium: Vital for strong bones and teeth, as well as nerve function.
- Magnesium: Supports muscle and nerve function, and helps regulate blood pressure.
- Potassium: Helps regulate fluid balance, muscle contractions, and nerve signals.
Also read: What is the Best Peptide for Bone Health – A complete Guide!
Trace Minerals:
These include iron, zinc, copper, selenium, and iodine, which are required in smaller amounts but are just as important.
- Iron: Necessary for producing hemoglobin, which carries oxygen in the blood.
- Zinc: Supports immune function, wound healing, and DNA synthesis.
- Selenium: Plays a role in protecting the body from oxidative stress.
The Importance of Micronutrients for Health:
Micronutrients are essential for the body’s biochemical reactions. Without adequate intake of these nutrients, vital bodily functions would be compromised. Here’s a closer look at why these nutrients are so important:
Supporting Immune Function:
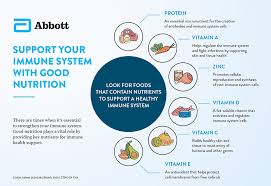
Your immune system relies on a range of vitamins and minerals to function efficiently. For example, vitamin C acts as an antioxidant, which helps protect cells from damage. It also boosts the production of white blood cells, which are critical in defending the body against infections. Zinc also plays a significant role in immune response by supporting the production of immune cells and helping wounds heal faster.
Promoting Bone Health:
Micronutrients such as calcium, vitamin D, and magnesium are vital for bone health. Calcium forms the building blocks of bones, while vitamin D helps the body absorb calcium. Magnesium works together with calcium to ensure proper bone density. Deficiencies in any of these nutrients can lead to weak bones, increasing the risk of fractures and osteoporosis, especially as you age.
Maintaining Energy Levels:
Many B vitamins, such as B12, B6, and B9 (folate), are involved in energy production by helping the body convert carbohydrates, fats, and proteins into usable energy. They are also critical for the production of red blood cells, which carry oxygen throughout the body. Without enough of these vitamins, you may feel tired, weak, and fatigued.
Cognitive Function and Mental Health:
Micronutrients like omega-3 fatty acids, iron, iodine, and zinc are essential for brain development and function. Iron, for example, helps transport oxygen to the brain, which is necessary for concentration and cognitive performance. Zinc and omega-3 are linked to improved memory and mood, while deficiencies in these nutrients can lead to impaired cognitive function and an increased risk of depression and anxiety.
Also read: What Health Literary Resources Are In New York City- A Comprehensive Guide!
Common Deficiencies in Micronutrients:
Despite their importance, micronutrient deficiencies are widespread, affecting millions of people worldwide. Here are some of the most common deficiencies:
Vitamin D Deficiency:
A lack of vitamin D can lead to weakened bones and muscles. People who live in regions with limited sunlight, have darker skin, or spend most of their time indoors are at higher risk of vitamin D deficiency. Symptoms may include fatigue, bone pain, and frequent infections.
Iron Deficiency:
Iron deficiency is one of the most common nutrient deficiencies worldwide. It can result in anemia, a condition where the body doesn’t produce enough healthy red blood cells to carry oxygen. Symptoms include tiredness, dizziness, and shortness of breath.
Vitamin B12 Deficiency:
Vitamin B12 is essential for nerve function and red blood cell production. Vegetarians, vegans, and older adults are at greater risk of deficiency since B12 is mainly found in animal products. A lack of B12 can lead to fatigue, weakness, and neurological problems like memory loss.
How to Ensure You Get Enough Micronutrients:
Achieving a balanced diet that includes all the necessary micronutrients is vital for good health. Here’s how you can ensure you’re getting enough:
Eat a Variety of Foods:
A diverse diet that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help you meet your micronutrient needs. Each food group contains different micronutrients, so eating a variety of foods ensures that you get a broad spectrum of vitamins and minerals.
Focus on Nutrient-Dense Foods:

Nutrient-dense foods are those that provide a high amount of vitamins and minerals relative to their calorie content. These include leafy greens, berries, nuts, seeds, fish, and legumes. Avoid relying on processed foods, which may be high in calories but low in nutrients.
Consider Supplements:
In some cases, it may be difficult to meet your micronutrient needs through diet alone. For example, people with specific health conditions, pregnant women, or older adults may require supplements. Always consult a healthcare provider before taking any supplements to avoid excess intake, which can be harmful.
Micronutrients vs. Macronutrients: What’s the Difference?
Both macronutrients and micronutrients are essential for your body, but they have different roles. Macronutrients provide the energy needed for bodily functions, while micronutrients regulate those processes and ensure everything runs smoothly.
Macronutrients:
- Carbohydrates: The body’s primary source of energy.
- Proteins: Essential for tissue repair, enzyme production, and muscle growth.
- Fats: Store energy and support cell growth and brain function.
Micronutrients:
- Vitamins and Minerals: Help regulate metabolism, maintain nerve and muscle function, and support immune health.
The Role of Micronutrients in Disease Prevention:
Getting adequate micronutrients can reduce your risk of chronic diseases. For example:
- Vitamin D reduces the risk of osteoporosis.
- Antioxidants like vitamin C and vitamin E reduce the risk of chronic diseases by protecting cells from oxidative stress.
- Iron prevents anemia and ensures the body gets enough oxygen to its cells.
Also read: What Does Contract Work Mean In Mental Health Services – A Complete Guide!
FAQ’s
1. What are micronutrients?
Micronutrients are essential nutrients like vitamins and minerals required in small amounts to support vital body functions.
2. Why are micronutrients important?
They help regulate body processes, support immunity, maintain energy levels, and promote overall health.
3. What are the types of micronutrients?
Micronutrients are divided into vitamins (water- and fat-soluble) and minerals (major and trace minerals).
4. What happens if you lack micronutrients?
Deficiencies can lead to weakened immunity, poor bone health, cognitive issues, and chronic conditions like anemia.
5. How can I ensure enough micronutrients in my diet?
Eating a variety of nutrient-dense foods like fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins, and considering supplements if needed, ensures proper intake.
Conclusion
In conclusion, micronutrients are vital for overall health, supporting everything from immune function to cognitive performance. Deficiencies in these nutrients can lead to serious health problems, making it essential to maintain a balanced and nutrient-rich diet. Ensuring proper intake of both vitamins and minerals is key to promoting long-term well-being.
Related post
- Also read: When Does Nutex Health Inc Do Earnings Report Come Out – A Complete Guide!
- Also read: What is Tier 1 Home Health in Arkansas – A Complete Guide!
- Also read: Is Liquid Cotton Bad for Your Health – The Truth You Need to Know!