Magnesium welding rods release harmful fumes that can cause respiratory issues and skin burns. Safety measures like PPE and proper ventilation are essential for protection
Welding is a vital process in industries such as construction, manufacturing, and automotive repair. However, the welding of magnesium rods presents unique health hazards that must be understood and addressed to ensure the safety of workers.
This article will cover the health hazards associated with magnesium welding rods, safety measures to follow, and tips for protecting yourself in the workplace.
Understanding Magnesium Welding Rods:
What are Magnesium Welding Rods?
Magnesium welding rods are used to weld magnesium and magnesium alloys. Magnesium is known for its strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and ability to be easily machined. These characteristics make it an ideal material for welding applications in industries like aerospace, automotive, and electronics.
Magnesium welding rods are specifically designed for repairing magnesium parts or joining magnesium components together.However, welding magnesium comes with risks that differ from welding other metals like steel or aluminum. Magnesium welding produces fumes and particles that can pose serious health hazards if not properly controlled.
Why Use Magnesium Welding?
Magnesium welding is necessary for applications where lightweight materials are needed without sacrificing strength. In sectors such as aerospace, weight reduction is crucial for efficiency, and magnesium offers that advantage.
It also provides excellent heat dissipation, making it suitable for automotive parts like engine blocks and transmission cases. While magnesium offers clear benefits, it’s important to weigh those against the potential health risks involved in welding.
Health Hazards of Magnesium Welding Rods:
Fume Exposure:
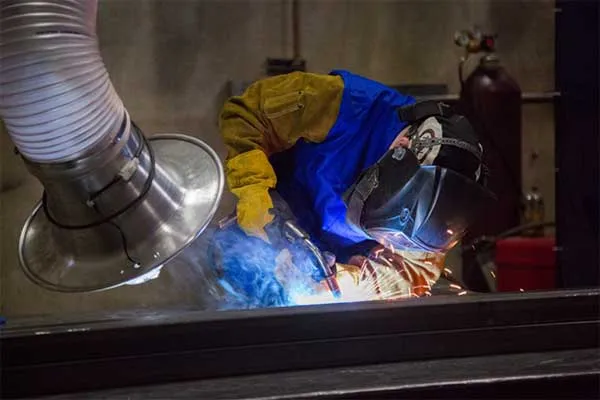

One of the most significant health risks when welding with magnesium rods is exposure to hazardous fumes. Magnesium burns at very high temperatures, and during welding, fumes containing magnesium oxide can be released into the air. Inhalation of these fumes can lead to a condition known as “metal fume fever,” which causes flu-like symptoms, including:
- Fever
- Chills
- Nausea
- Headache
- Fatigue
The symptoms usually appear within a few hours after exposure and can last for up to 48 hours. While metal fume fever is generally not life-threatening, repeated exposure to welding fumes without proper protection can have long-term health consequences.
Respiratory Issues:
Inhaling magnesium fumes and particles over long periods can lead to more severe respiratory conditions. Chronic exposure may cause permanent damage to the lungs, including diseases such as:
- Bronchitis
- Asthma-like symptoms
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
These conditions can significantly reduce a worker’s quality of life and may require ongoing medical treatment. It’s essential to use proper ventilation and respiratory protection to minimize inhalation risks.
Eye Irritation:
Magnesium welding also presents the risk of eye irritation. The intense ultraviolet (UV) light emitted during welding can cause “arc eye,” a painful condition resulting from corneal burns. Symptoms of arc eye include:
- Red, watery eyes
- Sensitivity to light
- Gritty sensation in the eyes
Welders should always wear appropriate eye protection, such as a welding helmet with a filter shade, to prevent arc eye and other eye injuries.
Skin Burns:
Welding with magnesium can cause severe skin burns if proper precautions are not taken. Magnesium burns at extremely high temperatures, and direct contact with molten metal can result in serious burns.
Even indirect exposure to UV radiation from the welding process can cause skin burns, similar to sunburns. It’s important to wear flame-resistant clothing, gloves, and other protective gear to avoid skin injuries.
Fire and Explosion Hazards:
Magnesium is highly flammable, and welding with magnesium rods can pose fire and explosion hazards. Magnesium burns at a high temperature and reacts violently with water and other materials, potentially leading to dangerous fires or explosions in the workplace.
Special fire suppression methods are needed to extinguish magnesium fires, as using water or foam can make the fire worse.
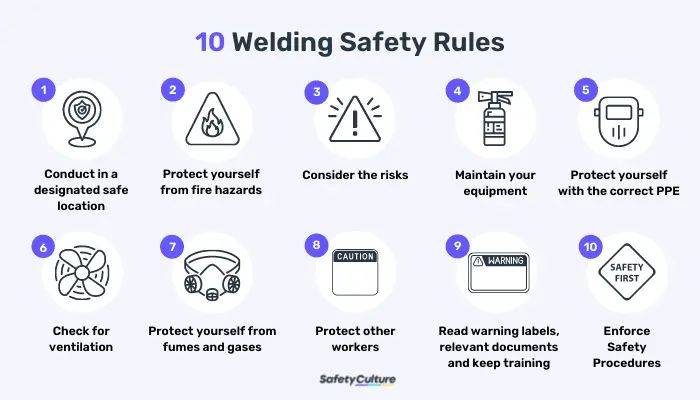
Safety Measures for Welding with Magnesium Rods:
Proper Ventilation:
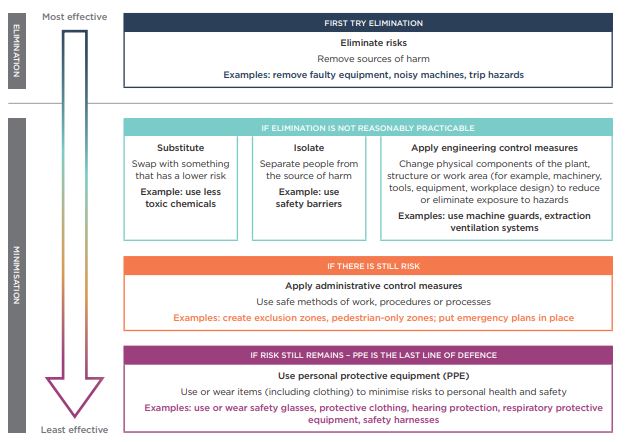
Adequate ventilation is critical when welding with magnesium rods to reduce the risk of fume exposure. Work in well-ventilated areas, preferably outdoors or in environments with exhaust systems that can effectively remove hazardous fumes from the air. If local ventilation is not sufficient, personal protective equipment (PPE), such as a respirator, should be used.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
Welders should always wear appropriate PPE to protect against the health hazards of magnesium welding. Key protective gear includes:
- Respirators: To filter out harmful fumes and particulates, especially in areas with limited ventilation.
- Welding helmets: To protect the eyes from UV radiation and prevent arc eye.
- Flame-resistant clothing: To reduce the risk of skin burns.
- Gloves: To protect the hands from heat and direct contact with molten metal.
- Boots: To prevent foot injuries from falling debris or molten metal.
Fire Safety Precautions:
Due to the flammability of magnesium, it’s essential to take precautions to minimize the risk of fires or explosions. These include:
- Keeping flammable materials and liquids away from the welding area.
- Having fire extinguishers designed for magnesium fires (Class D fire extinguishers) nearby.
- Avoiding the use of water or foam to extinguish magnesium fires.
Controlled Environment:
Ensure that welding with magnesium is done in a controlled environment. This means:
- Maintaining a clean workspace free of flammable materials.
- Avoiding welding near water sources or areas with excessive moisture, as magnesium can react dangerously with water.
- Using specialized equipment designed for handling magnesium, especially in high-temperature situations.
Long-Term Health Considerations:
Regular Medical Checkups:
Workers who regularly weld with magnesium rods should undergo periodic medical checkups to monitor their respiratory health. Early detection of respiratory issues can prevent more serious conditions from developing over time. If any symptoms such as shortness of breath, persistent coughing, or chest pain occur, it’s essential to seek medical attention immediately.
Monitoring Air Quality:
Employers should conduct regular air quality tests to ensure that fume levels in the workplace do not exceed the recommended limits set by occupational safety organizations. This is especially important in indoor welding environments, where fumes can accumulate more quickly.
Education and Training:
Proper education and training for welders are crucial in minimizing the risks associated with magnesium welding. Workers should be trained on the specific hazards of welding with magnesium rods and how to protect themselves. This includes understanding the importance of ventilation, PPE, and fire safety.
FAQ’S
1. What are the health risks of welding with magnesium rods?
The health risks include exposure to harmful fumes, respiratory issues, eye irritation, skin burns, and fire hazards.
2. How can fume exposure from magnesium welding be minimized?
Fume exposure can be minimized by working in well-ventilated areas and using appropriate respirators.
3. What personal protective equipment (PPE) should be used for magnesium welding?
PPE for magnesium welding includes respirators, welding helmets, flame-resistant clothing, gloves, and boots.
4. Why is magnesium welding dangerous in terms of fire hazards?
Magnesium is highly flammable and reacts violently with water, making fire and explosion risks significant.
5. What long-term health monitoring should be done for magnesium welders?
Regular medical checkups and air quality monitoring are important to detect early respiratory issues and ensure safe working conditions.
Conclusion
Magnesium welding presents significant health hazards, including exposure to harmful fumes, respiratory issues, and severe burns. To ensure safety, it is crucial to implement effective ventilation, use appropriate personal protective equipment, and adhere to fire safety precautions. Regular medical checkups and proper training are essential for minimizing risks and protecting workers in the long term.




