Yes, healthcare providers can become psychiatrists, but they must complete medical school and residency training, which requires significant dedication.
In this article, we will explore the qualifications, responsibilities, and journey to becoming a psychiatrist. We’ll provide a clear understanding of what it takes to enter this important profession.
The Function of a Psychiatrist Explained:
The Functions and Duties of a Psychiatrist:
A psychiatrist is a medical doctor who focuses on identifying and treating mental health disorders.They have the training to prescribe medications and often combine this with therapeutic approaches. Unlike psychologists, psychiatrists can address both the medical and psychological aspects of mental health. Their expertise is essential for managing conditions like depression, anxiety, and schizophrenia.
Why Are Psychiatrists Important?
Psychiatrists are crucial in the mental health care system, providing support for individuals with various mental illnesses. They diagnose conditions such as bipolar disorder, anxiety disorders, and schizophrenia, offering a blend of medication management and therapy. This dual approach helps patients achieve better mental health outcomes and improve their quality of life.
By addressing both the biological and emotional aspects of mental health, psychiatrists play a vital role in promoting overall well-being.
Pathway to Becoming a Psychiatrist:
Educational Requirements:
To become a psychiatrist, one must first complete a series of educational steps:
- Bachelor’s Degree: The journey begins with a bachelor’s degree, typically in a related field like psychology, biology, or health sciences.
- Medical School: After obtaining a bachelor’s degree, aspiring psychiatrists must attend medical school, which generally takes four years. During this time, students learn about various aspects of medicine, including psychiatry.
- Residency Training: After medical school, graduates must complete a residency program in psychiatry. This usually lasts four years and provides hands-on experience in diagnosing and treating mental health disorders.
Also read: Who Will Pay For Articles On Health Food – Pays for Health Food Content!
Licensure and Certification:
After completing residency training, psychiatrists must obtain a medical license to practice in their state.This includes taking a series of exams.Additionally, many psychiatrists choose to become board-certified by the American Board of Psychiatry and Neurology, which requires passing an additional exam.
Can Health Care Providers Become Psychiatrists?
Defining Health Care Providers:
Health care providers encompass a broad range of professionals in the medical field, including doctors, nurses, physician assistants, and therapists. While some of these roles can lead to becoming a psychiatrist, others may require additional training.
Transitioning from Other Health Care Roles:
- Nurses: Registered nurses (RNs) can pursue further education to become nurse practitioners (NPs) specializing in psychiatry. NPs can provide some mental health services, prescribe medications, and work closely with psychiatrists.
- Physician Assistants (PAs): PAs can also work in mental health settings. However, they do not become psychiatrists unless they attend medical school and complete residency training.
- Psychologists: Clinical psychologists who hold a doctorate (Ph.D. or Psy.D.) in psychology cannot become psychiatrists without completing medical school and residency. However, they can provide therapy and assessment services.
Limitations and Considerations:
While health care providers can explore various roles in mental health, becoming a psychiatrist requires extensive education and training. This includes completing a medical degree, residency in psychiatry, and obtaining board certification. Additionally, not all health care providers may have the resources or desire to commit to this lengthy process, limiting their ability to practice as psychiatrists.
Responsibilities of a Psychiatrist:

Patient Assessment:
Psychiatrists perform comprehensive evaluations to understand a patient’s mental health. They gather detailed information about medical history, symptoms, and lifestyle factors. This thorough assessment is crucial for making accurate diagnoses and determining appropriate treatment.
Developing Treatment Plans:
After diagnosing a condition, psychiatrists create tailored treatment plans for each patient. These plans often incorporate medication, therapy, or a combination of both. Collaborating with patients to set treatment goals ensures a personalized approach to mental health care.
Medication Management:
Psychiatrists have the authority to prescribe medications for mental health disorders. They closely monitor how patients respond to these medications, making adjustments as necessary. This ongoing management is essential for achieving optimal treatment outcomes.
Ongoing Support and Therapy:
Many psychiatrists offer therapy in addition to medication management. They may employ techniques such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) to provide holistic care. Collaborating with other mental health professionals enhances the support provided to patients.
Also read: A List Of Global Health Dentist – Improving Oral Health Worldwide!
Challenges Faced by Psychiatrists:
- Stigma Around Mental Health: Stigma surrounding mental health issues persists, preventing many from seeking help. Psychiatrists work to combat these misconceptions by educating the public and advocating for their patients to promote understanding and acceptance.
- Managing Complex Cases: Psychiatrists often deal with complex cases, including patients with co-occurring mental health and substance use disorders. Successfully managing these cases requires advanced clinical skills and a personalized approach to treatment.
- Burnout and Self-Care: The emotional demands of mental health care can lead to burnout among psychiatrists. It’s essential for them to prioritize self-care strategies to maintain their well-being, ensuring they provide the best support for their patients.
Can Other Healthcare Providers Become Psychiatrists?

Yes, Other Healthcare Providers Can Become Psychiatrists:
Yes, other healthcare providers can transition into psychiatry, but this journey requires a substantial commitment to education and training. While many professionals in the healthcare field have a strong foundation in patient care, becoming a psychiatrist involves specific steps that must be followed.
Necessary Educational Path:
To become a psychiatrist, healthcare professionals, such as nurses, psychologists, or social workers, must first complete a medical degree (either an MD or DO). This typically involves four years of medical school, where they learn about various aspects of medicine, including mental health.
Following medical school, they must complete a residency in psychiatry, which usually lasts about four years. This residency provides in-depth training in diagnosing and treating mental health disorders.
Commitment to Further Education:
It’s crucial to recognize that the path to becoming a psychiatrist is demanding. It requires not only years of education but also practical experience in clinical settings. Those transitioning from other healthcare roles need to be prepared for a rigorous academic and emotional journey, as they will be responsible for understanding complex mental health issues and providing comprehensive care to their patients.
Also read: Golden Retriever Health Issues – Common Health Problems Explained!
FAQ’s
1. What qualifications are needed to become a psychiatrist?
To become a psychiatrist, one must complete a bachelor’s degree, attend medical school, and finish a residency in psychiatry. Additionally, obtaining a medical license and board certification is required.
2. Can registered nurses become psychiatrists?
Yes, registered nurses can transition to become psychiatrists by pursuing further education to earn a medical degree and completing a psychiatry residency.
3. What is the role of a psychiatrist?
Psychiatrists diagnose and treat mental health disorders, prescribing medications and providing therapy to help patients manage their conditions effectively.
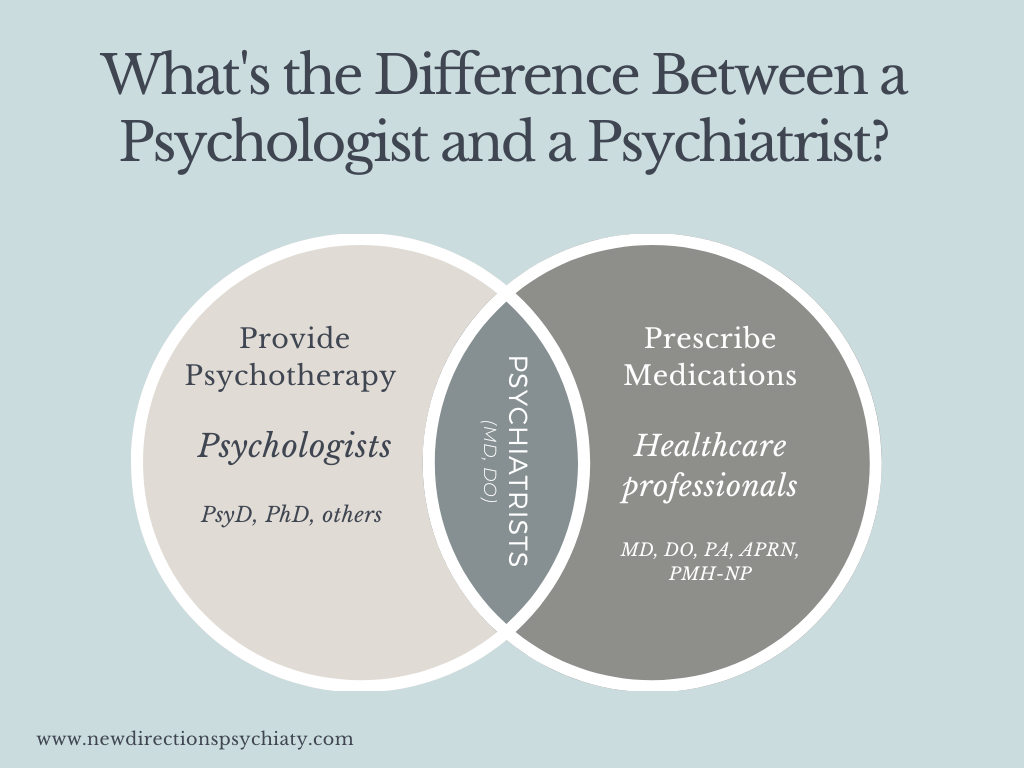
4. Are psychiatrists the same as psychologists?
No, psychiatrists are medical doctors who can prescribe medication, while psychologists typically focus on therapy and counseling without prescribing medication.
5.What difficulties do psychiatrists encounter?
Psychiatrists often deal with stigma surrounding mental health, complex cases, and the risk of burnout due to the emotional demands of their work.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the journey to becoming a psychiatrist is rigorous, requiring extensive education and training, including medical school and residency. Psychiatrists play a vital role in the mental health care system, addressing both medical and psychological aspects of mental health disorders. Their expertise not only aids in effective treatment but also helps to combat stigma and improve overall mental well-being.
Related post
- Also read: Intermountain Health Ironman 70.3 Triathlon Where Is Swimming Course – A Complete Guide!
- Also read: Ethical Issues in Health Communication: Health-Related News Sourcing Practices – Ethical Considerations in Health News!
- Also read: Is The Source Sacramento In The Sierra Health Foundation Building – A Complete Guide!




